TypeScript : Fewer Bugs, Better Code
Typescript guide for beginners with the best simple examples in react components.

Understanding TypeScript : Why it matters and How it helps Developers
After learning JavaScript, I came across TypeScript. At first, I wasn’t sure if it was really necessary. I thought, “Why not just be careful and manually check the type of each variable?” That seemed reasonable for small projects, and to some extent, it worked.
But while working as an intern at Ewan Byte, I was part of a large project and that’s when I realised how unrealistic that approach was. As the codebase grew, manually tracking every variable type became messy and time-consuming. Finding a type-related bug at the end of development was frustrating and costly. That’s when I truly understood why TypeScript exists and Type structures must be consistent between backend and frontend for proper communication.
What is TypeScript ?
TypeScript is a strongly typed programming language that builds on JavaScript by adding static type definitions. It introduces type checking at compile time, helping developers catch errors early. Its main benefit is highlighting unexpected behaviour in code, reducing the chance of bugs.
Why is TypeScript required?
JavaScript is flexible, but that flexibility often leads to hidden errors. Without type checking, code might break at runtime — right when users are interacting with it. JavaScript provides types like string and number, but it doesn’t ensure consistent use. TypeScript does.
It helps by:
- Catching errors during compilation, before execution.
- Making code easier to understand with explicit types.
- Improving team collaboration with clear data structures.
- Enhancing the developer experience with better auto-completion and error hints.
GENERAL TERMS : type , interface , union , generics
typeandinterfaceare WAYS TO DEFINE types- Union is a FEATURE OF types
- Generics are TEMPLATES FOR types
Types and Interface
We can define an object’s structure in TypeScript using either an interface or a type . Both specify what properties an object should have and their types.
Using Interface
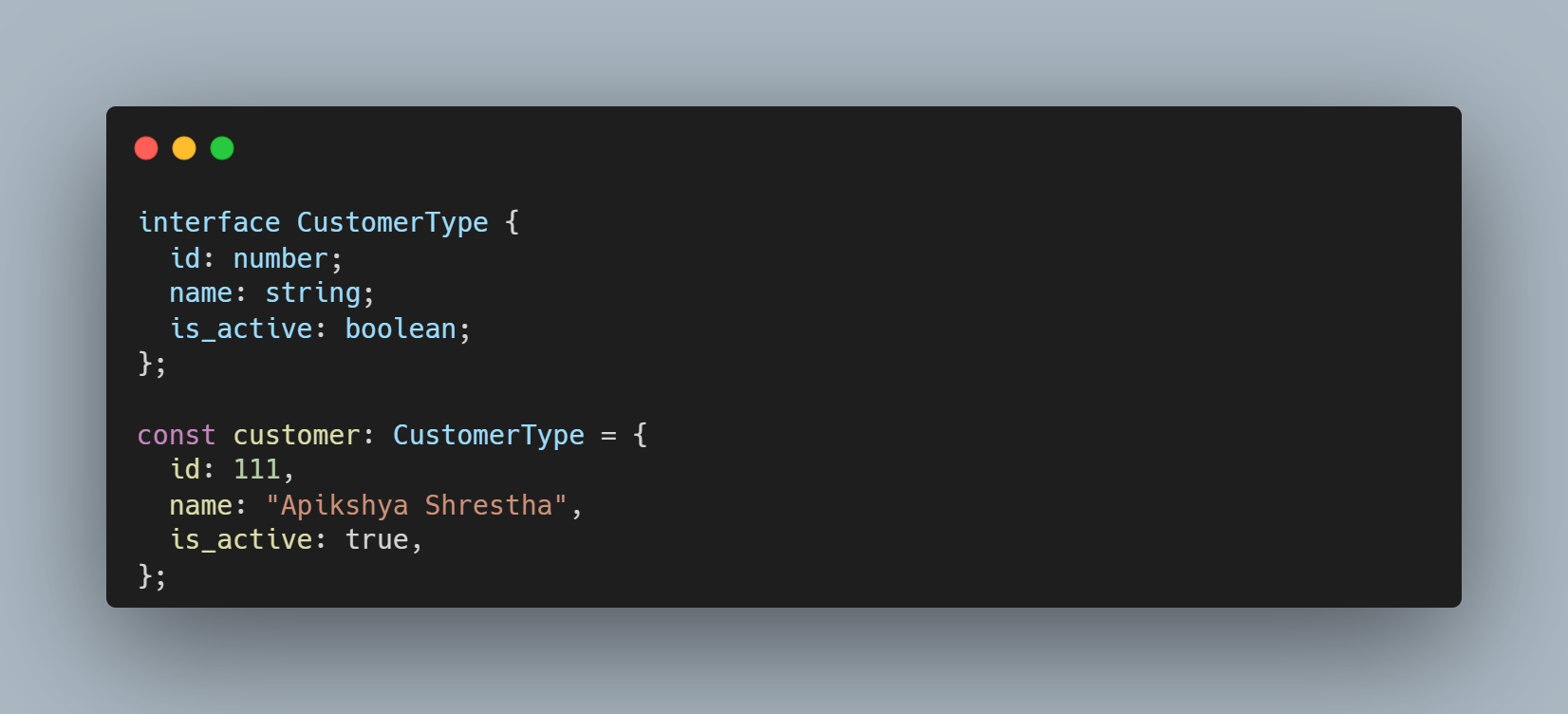
interface CustomerType: Declares a new interfaceid: number: Requires a numericidpropertyname: string: Requires a stringnamepropertyis_active: boolean: Requires a booleanis_activepropertyconst customer: CustomerType: Creates a constant variablecustomerthat must follow theCustomerTypeinterface- The object must include all three properties with the correct types
Using Type
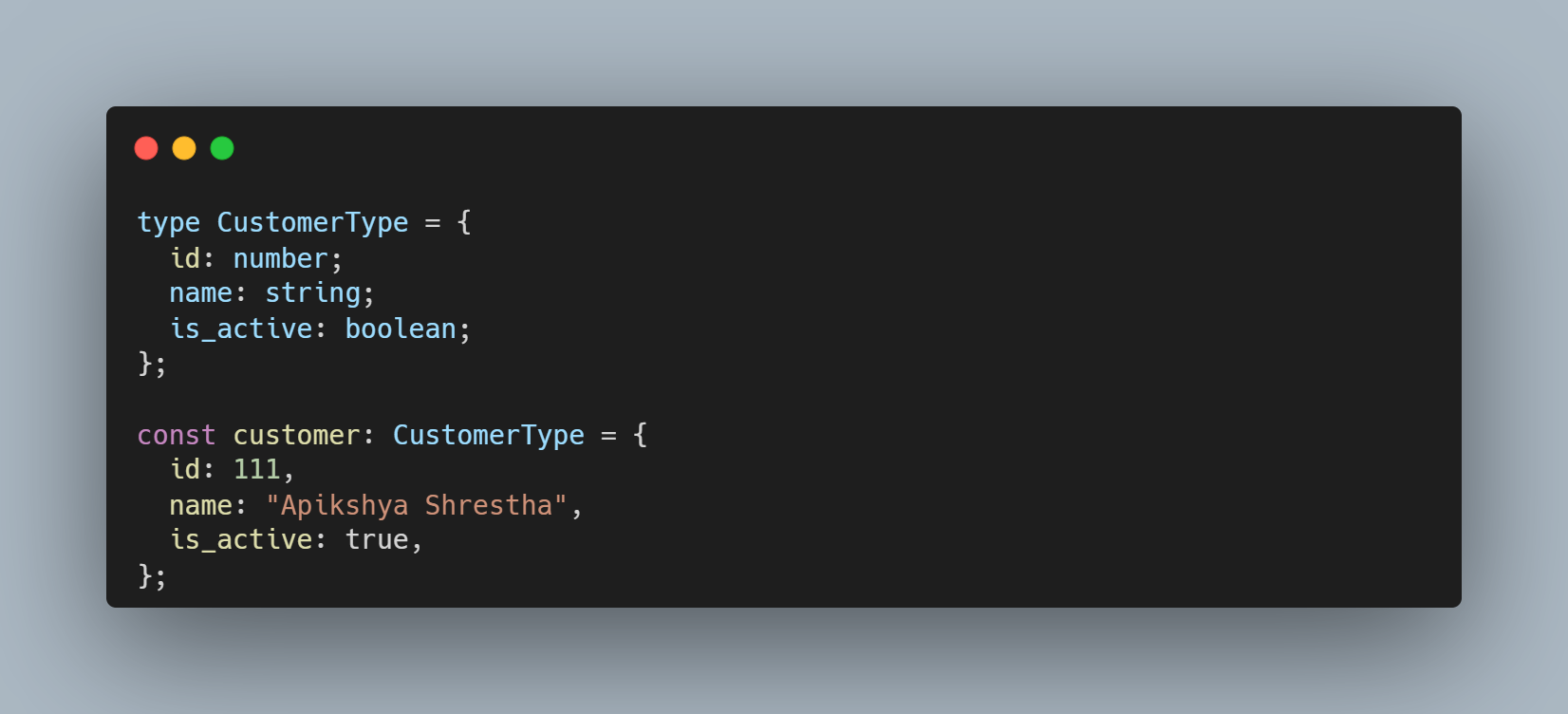
type CustomerType: Declares a new typeconst customer: CustomerType: Creates a constant variablecustomerthat must follow theCustomerTypetype
What to use interface or type?
Use interface when we need to:
- Object-oriented design with
extends - Better error messages
- Library/framework types
- Define object shape
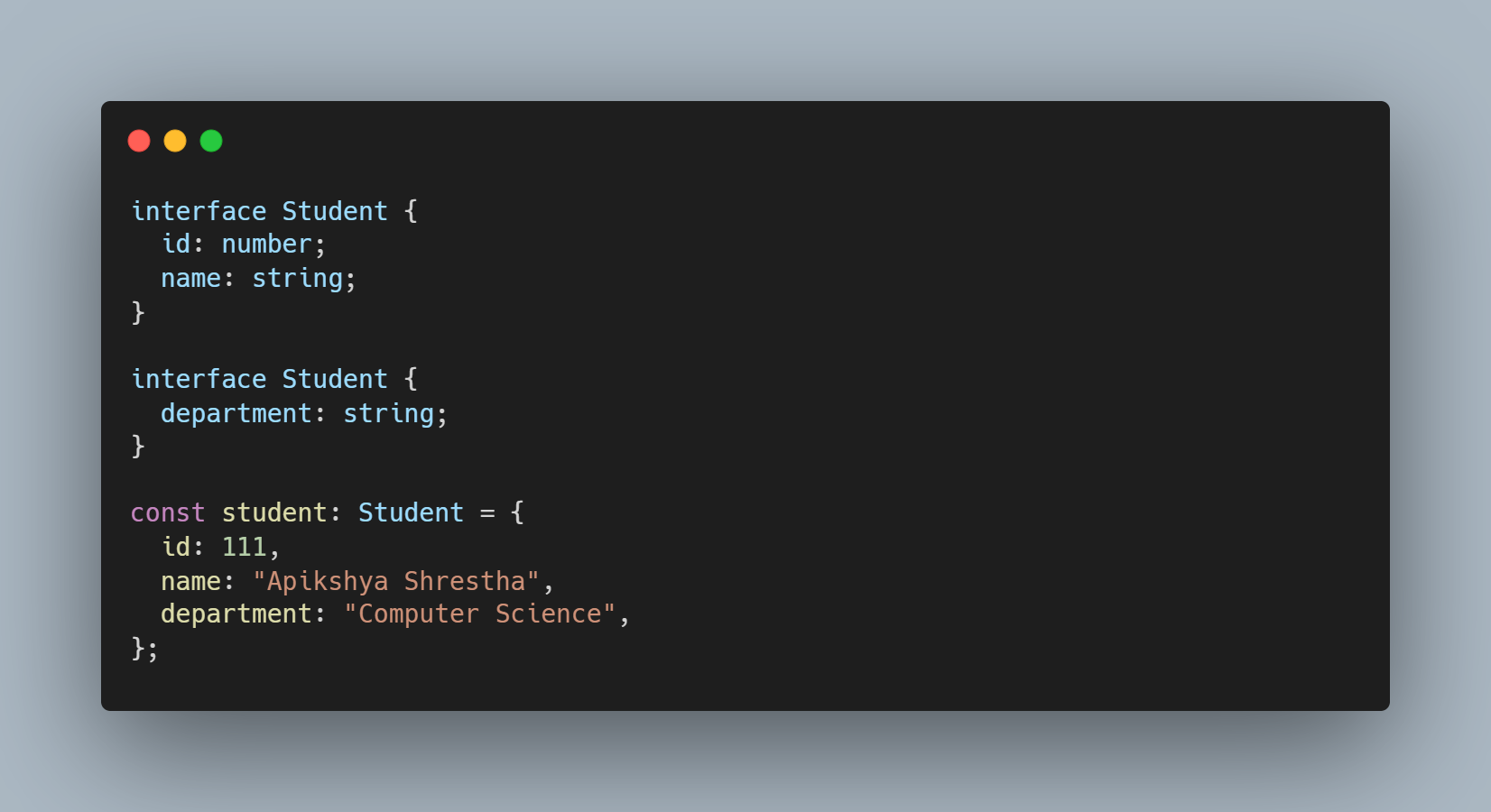
- Declaration Merging
Use type when we need:
- Complex type logic
- Functional programming patterns
- Union types
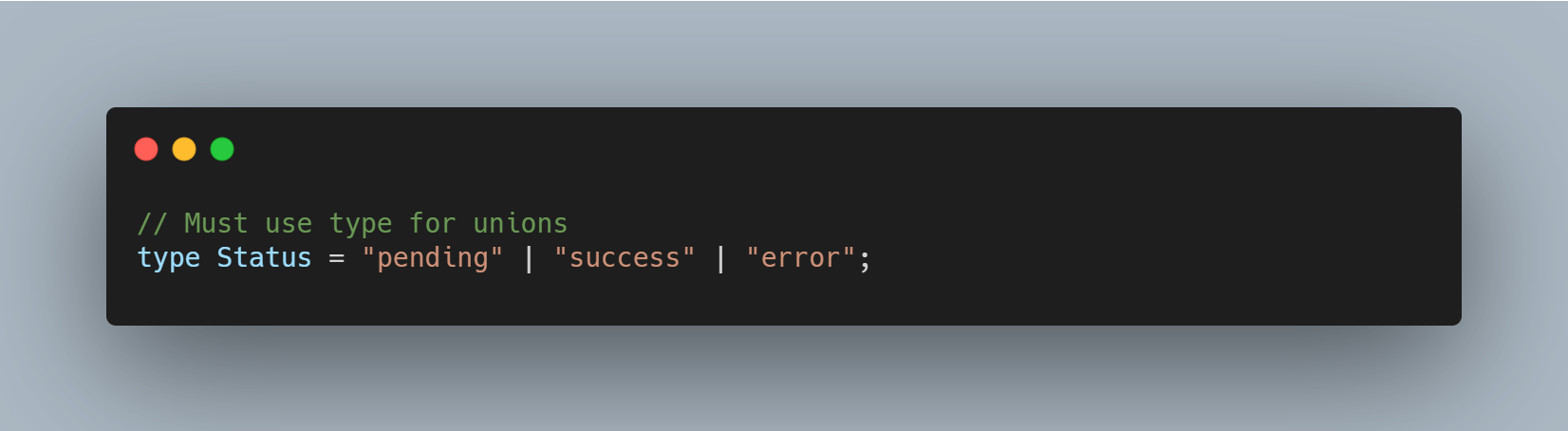
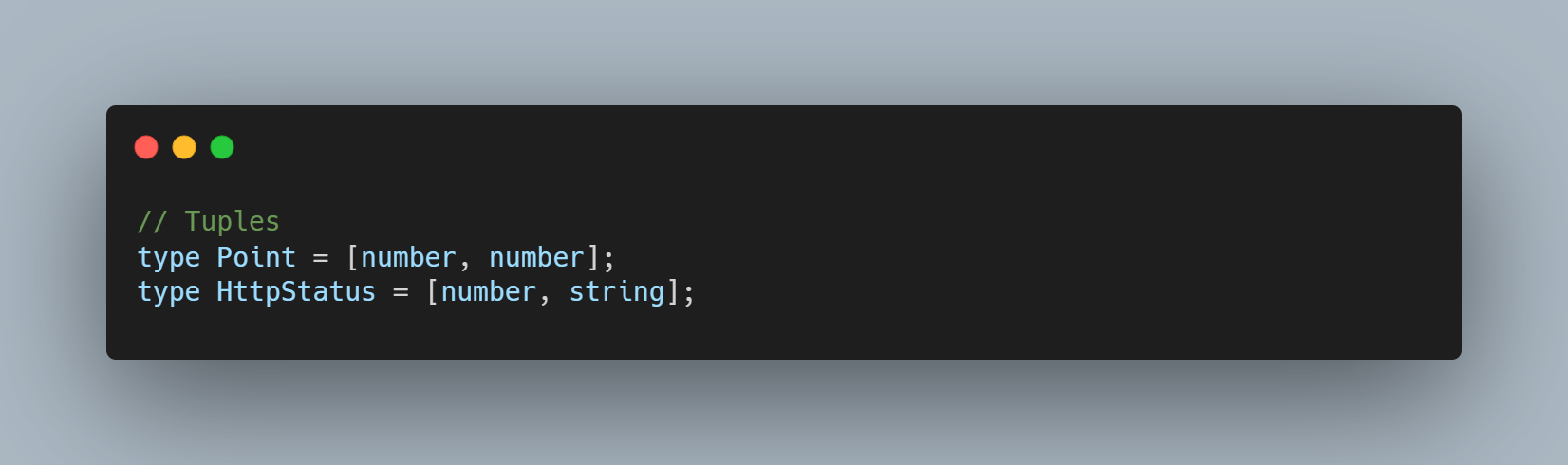
- Tuples
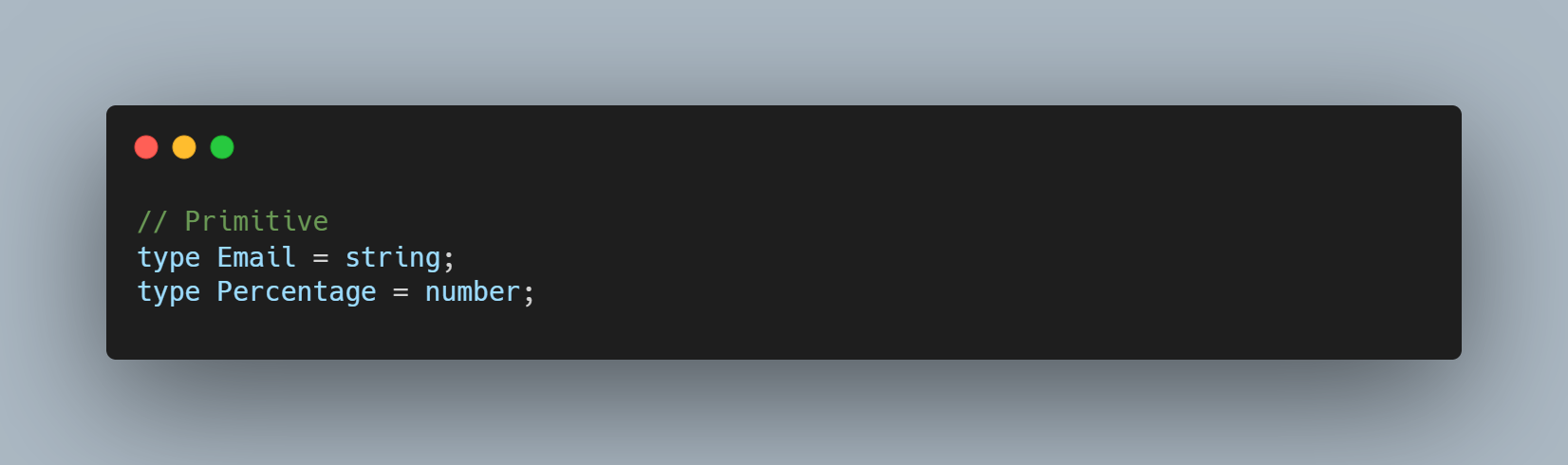
- Primitives
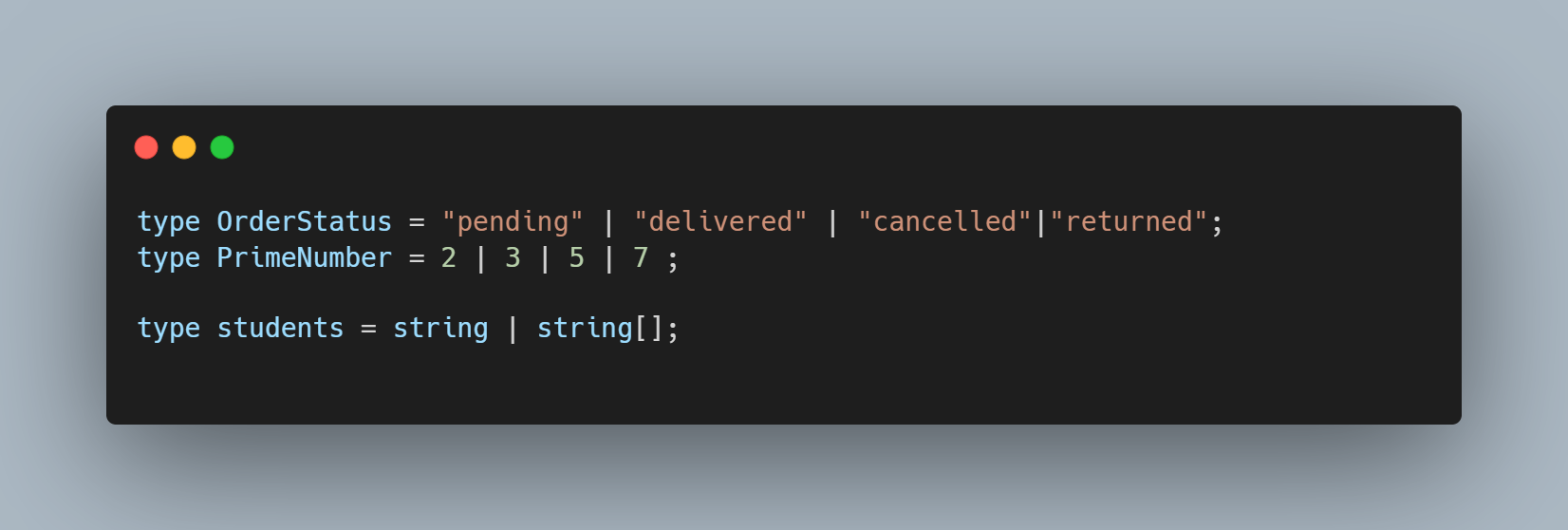
Union
Union describes the set of string or number literals that a value is allowed to be . Unions provide a way to handle different types too.
Generics
Generics create components that work with any type rather than a single specific type.
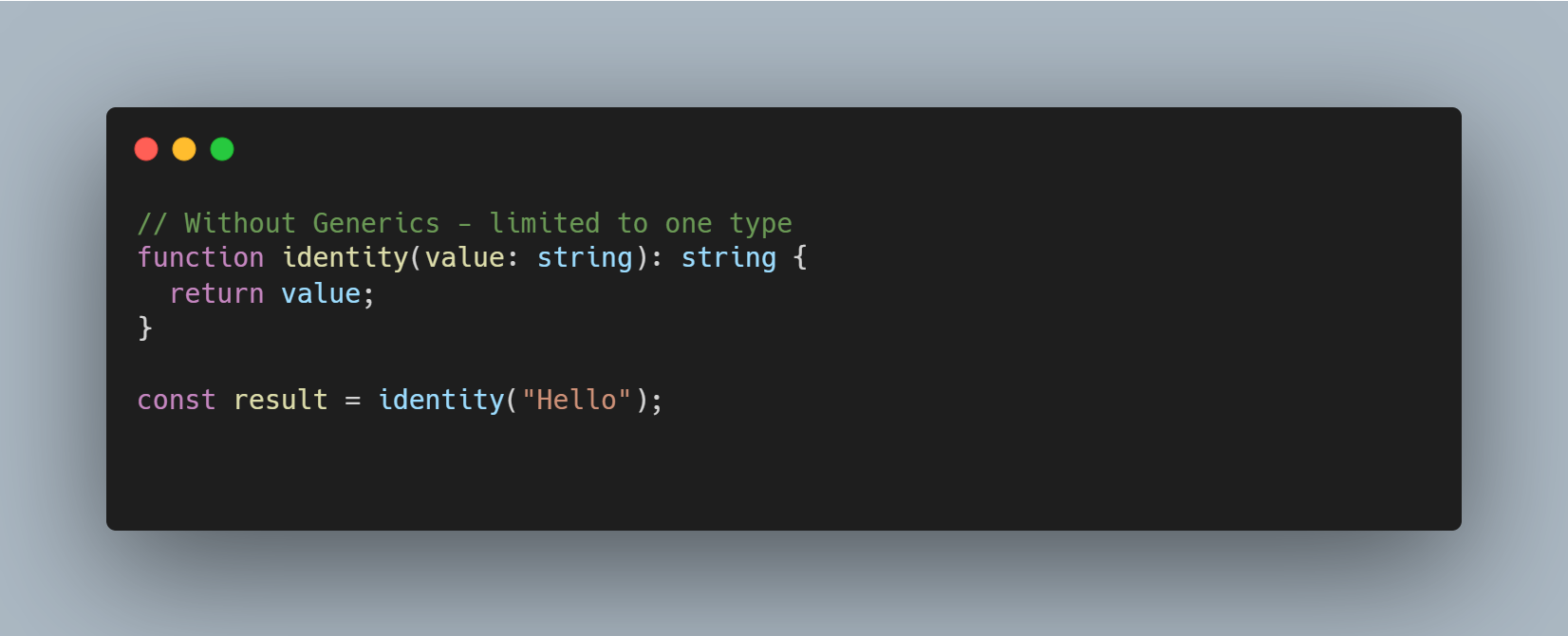
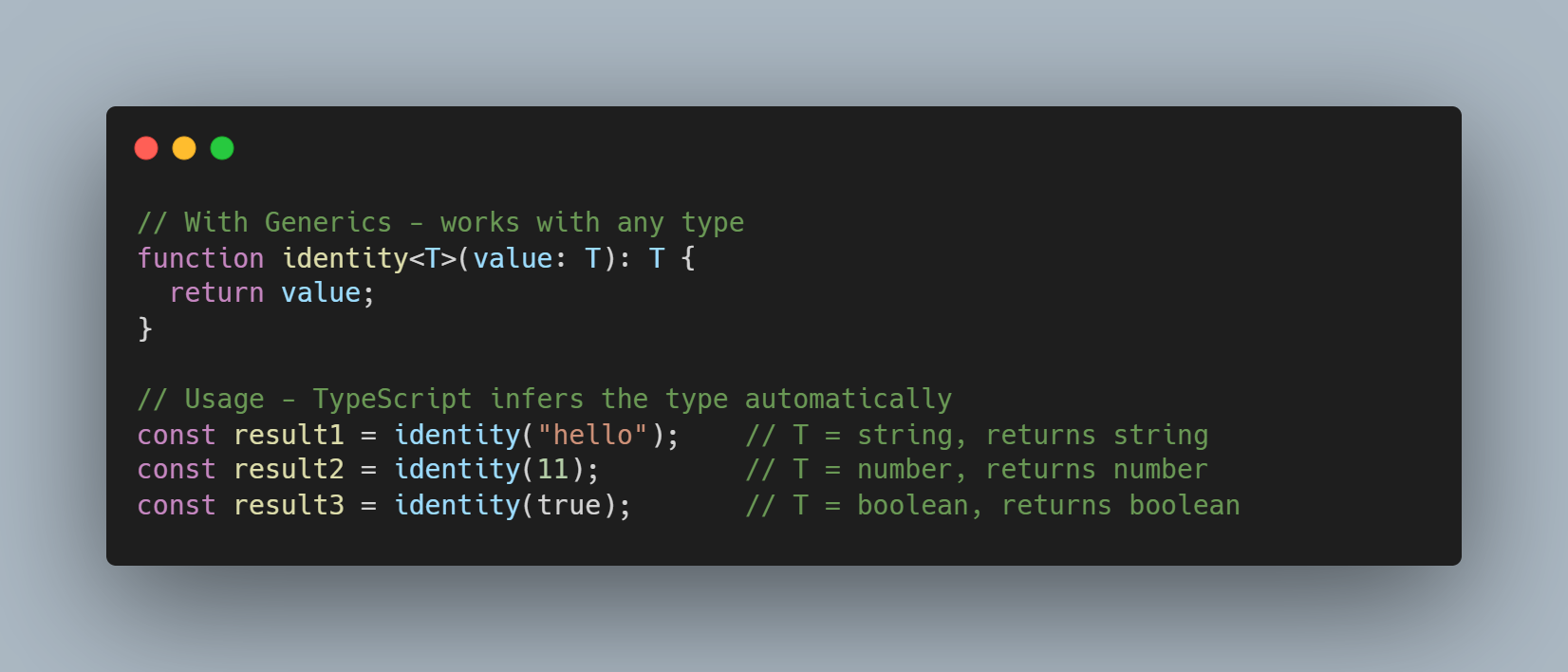
<T>= Type parameter (placeholder for actual type)value: T= Parameter of type T: T= Returns same type T
Extends in Interface
Interface use extends for inheritance between interfaces
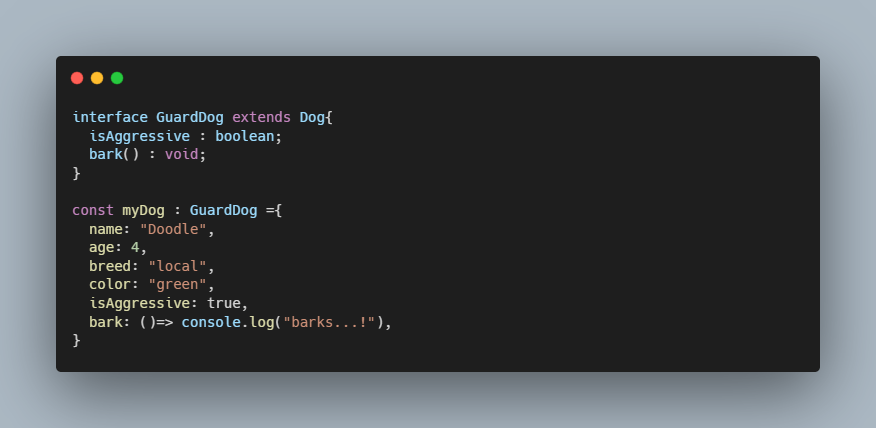
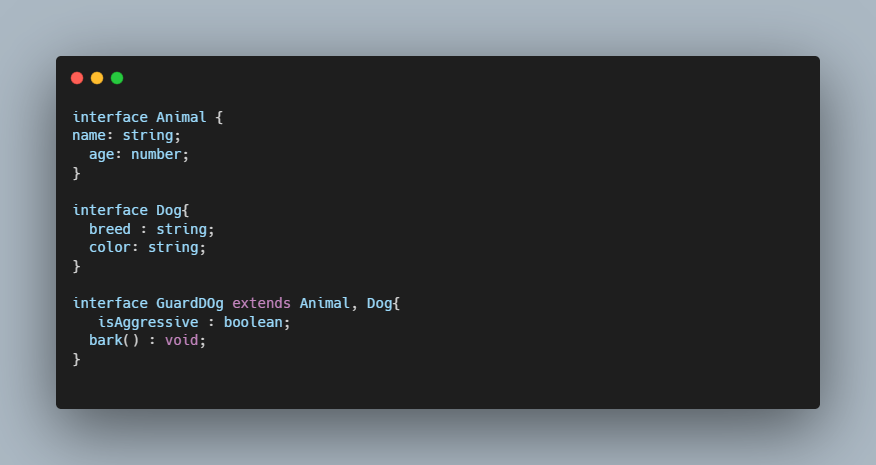
Extends in Type
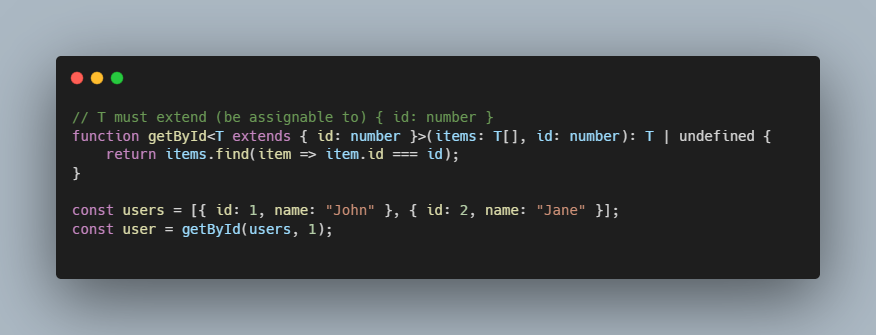
- Generic Constraint:
<T extends { id: number }>meansTmust be an object that has at least anidproperty of typenumber - Parameters:
items: T[]- an array of objects of typeTid: number- the id to search for
- Return Type:
T | undefined- returns either the found object orundefinedif not found
return items.find(item => item.id === id);
The function uses the array find() method to:
- Iterate through each item in the
itemsarray - Check if the item's
idproperty matches the providedidparameter - Return the first matching item, or
undefinedif no match is found
Type Inheritance (using intersection):
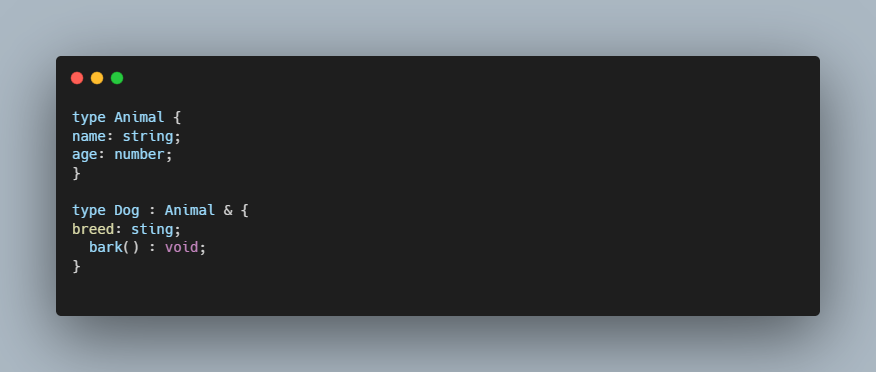
Type uses & (intersection) for combining types, but extends in generics and conditional types
Enum
Enums (enumerations) allow you to define a set of named constants.
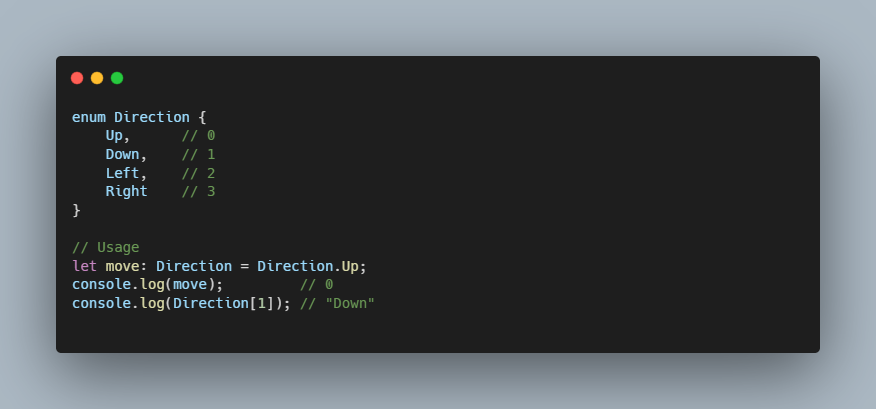
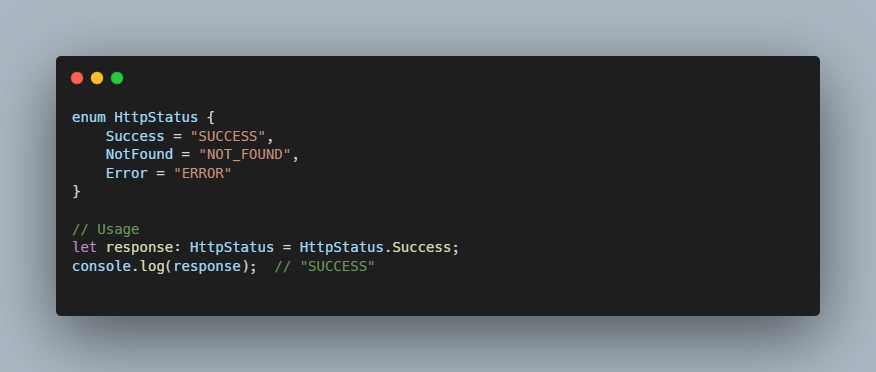
Interface with Enum
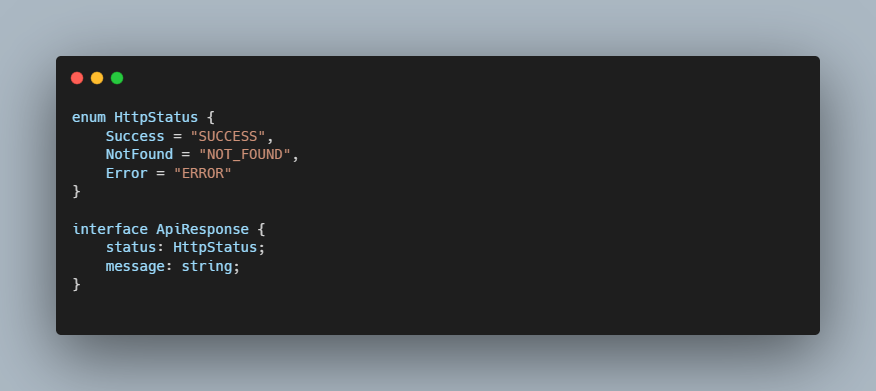
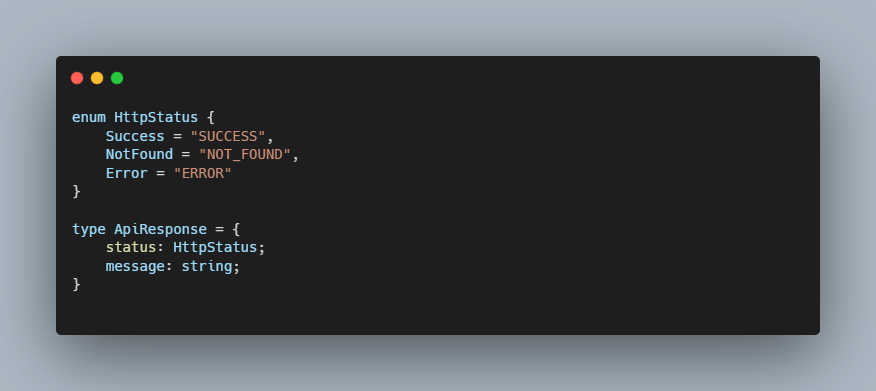
Type with Enum
Support for more complex generic constraints and conditional types will be covered in the upcoming documentation ... : )



Comments ()