A complete guide to authentication techniques in backend development.
What are the common Authentication Techniques ? · Basic Authentication · Token Based Authentication · Json Web Token (JWT) · Open authorization...

Authentication and API security is one of the most important concepts in today's modern applications. Many big tech companies like Google or Amazon uses some strong Authentication mechanisms within their internal systems to prevent or mitigate attacks on exposed or internal APIs.
What is authentication ?
Authentication is the process of verifying a user's identity before allowing them to access an application or any system. This answers to the question.
👉 Is the user really who they claim to be ?
This normally happens before authorization, which decides what the user should do.
The most common authentication techniques.
- Basic authentication.
- Token based authentication.
- JWT based authentication.
- OAuth authentication.
1 - Basic authentication.
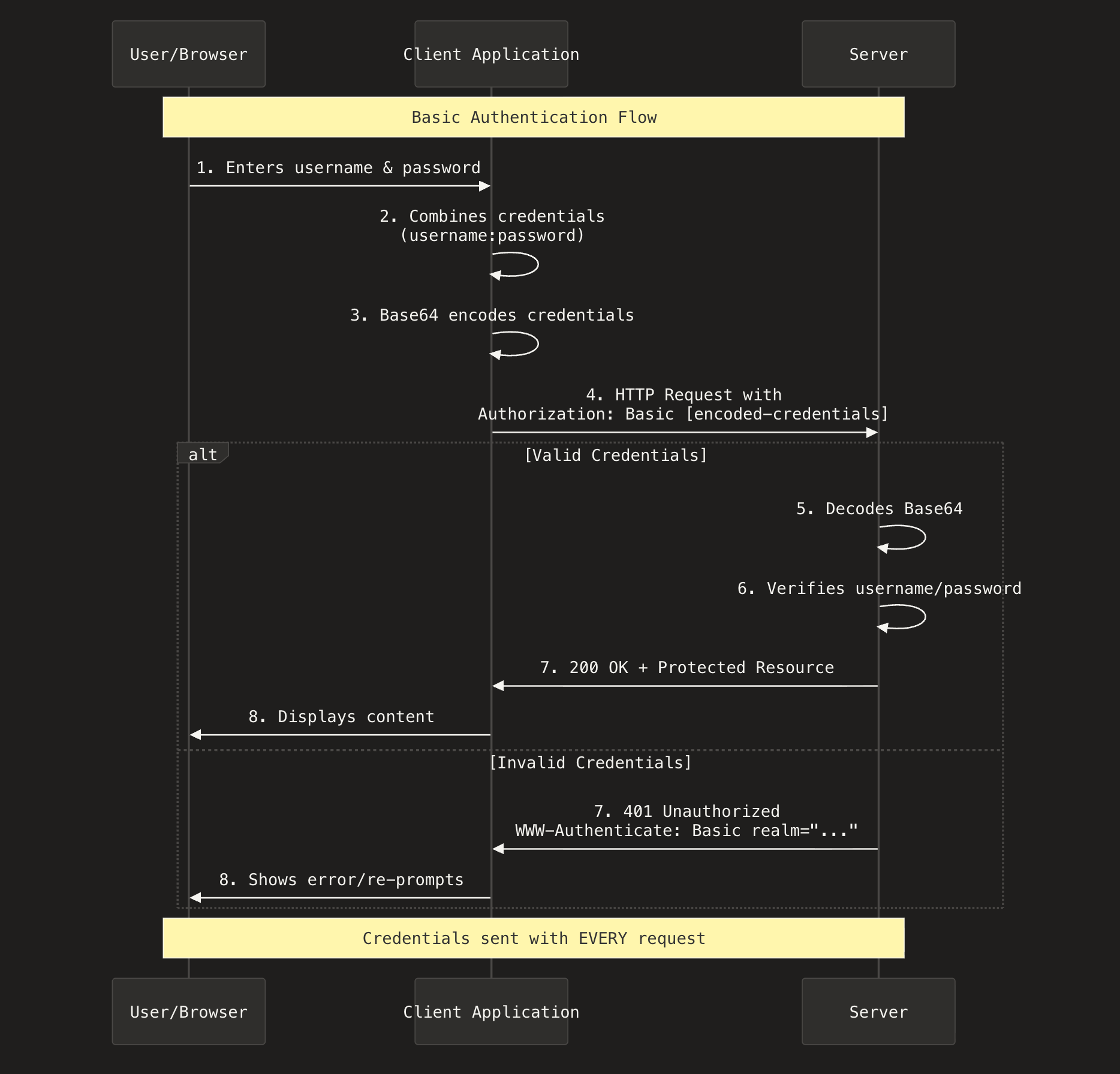
Basic authentication is one of the oldest and simplest authentication mechanisms. It works by sending username and password on every requests. Each requests includes an Authorization headers in the format Authorization: Basic <base64EncodedString> in which the base64EncodedString is the encoded format of username:password.
🔐 Basic Authentication: The Easiest Explanation
Imagine you go to the gate of a building.
The guard asks:
👉 “What is your username?”
👉 “What is your password?”
You tell him both.
He checks → lets you in.
Now imagine every time you enter the building — even if you went out for 1 minute the guard again asks for your username + password.
That is Basic Authentication.
Every request → you must send username + password again.
How it Works.
- The user (client) enters username + password and sends HTTP request to the server.
- The client converts the username:password into base64 encoded string. (base64 is not an encryption, it encodes only the text.).
- The request is sent with Authorization header like this.
Authorization: Basic c2FqYW46cGFzc3dvcmQxMjM=- The HTTP server now checks weather the request contains the authorization header and decodes the base64 string to get original username and password.
- If the credentials are valid then the server returns a 201 OK response, else the server returns 401 Unauthorized.
NOTE: Basic auth are not considered as secure since the base64 encoded are easily reversible, means anyone can decode the credentials unless they are used with HTTPS/S.
Where Basic auth mostly used ?
- Basic auth are mostly used in internal systems within an organization where high level security is not required.
- Testing or staging environments for quick development.
- Internal tools or dashboards within a private network.
Sequence diagram of how basic authentication works.
2 - Token based authentication.
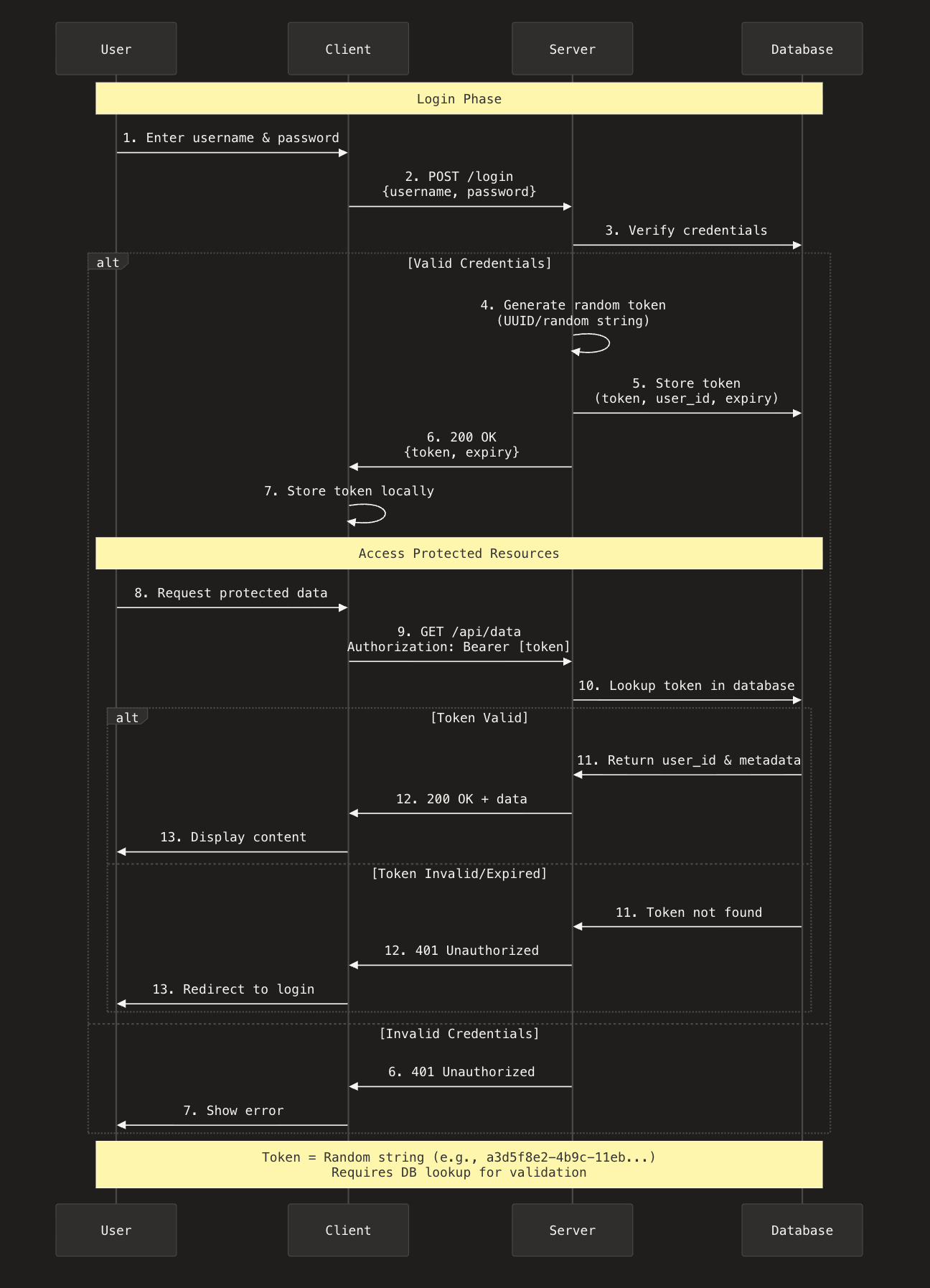
Unlike Basic Authentication, where the client must send the username and password with every request, in token-based authentication the client sends the credentials only once. After the server validates the username and password, it generates a unique token (a random string) and returns it to the client.
From this point on, the client no longer sends the username and password. Instead, every request includes the token, like this:
Authorization: Bearer <token>How it works.
- The client sends a login request with the username and password to the server.
- The server validates the credentials.
- If the credentials are invalid, the server returns:
401 Unauthorized. - If the credentials are valid, the server generates a token and returns:
200 OK (or 201, but 200 is more common)
- If the credentials are invalid, the server returns:
- The client now stores this token in local-storage or cookie and sends this token in every subsequent requests.
Authorization: Bearer <token>
- The server verifies the token:
- If the token is valid then server return 201 OK response.
- If the token is missing or invalid 401 Unauthorized.
The various types of token-based auth strategies.
JWT (JSON WEB TOKENS).
OAuth (Open authorization).
SAMP (Security assertions markup language)
OpenId connect
Sequence diagram of token-based authentication.
3 - JWT (JSON Web Tokens).
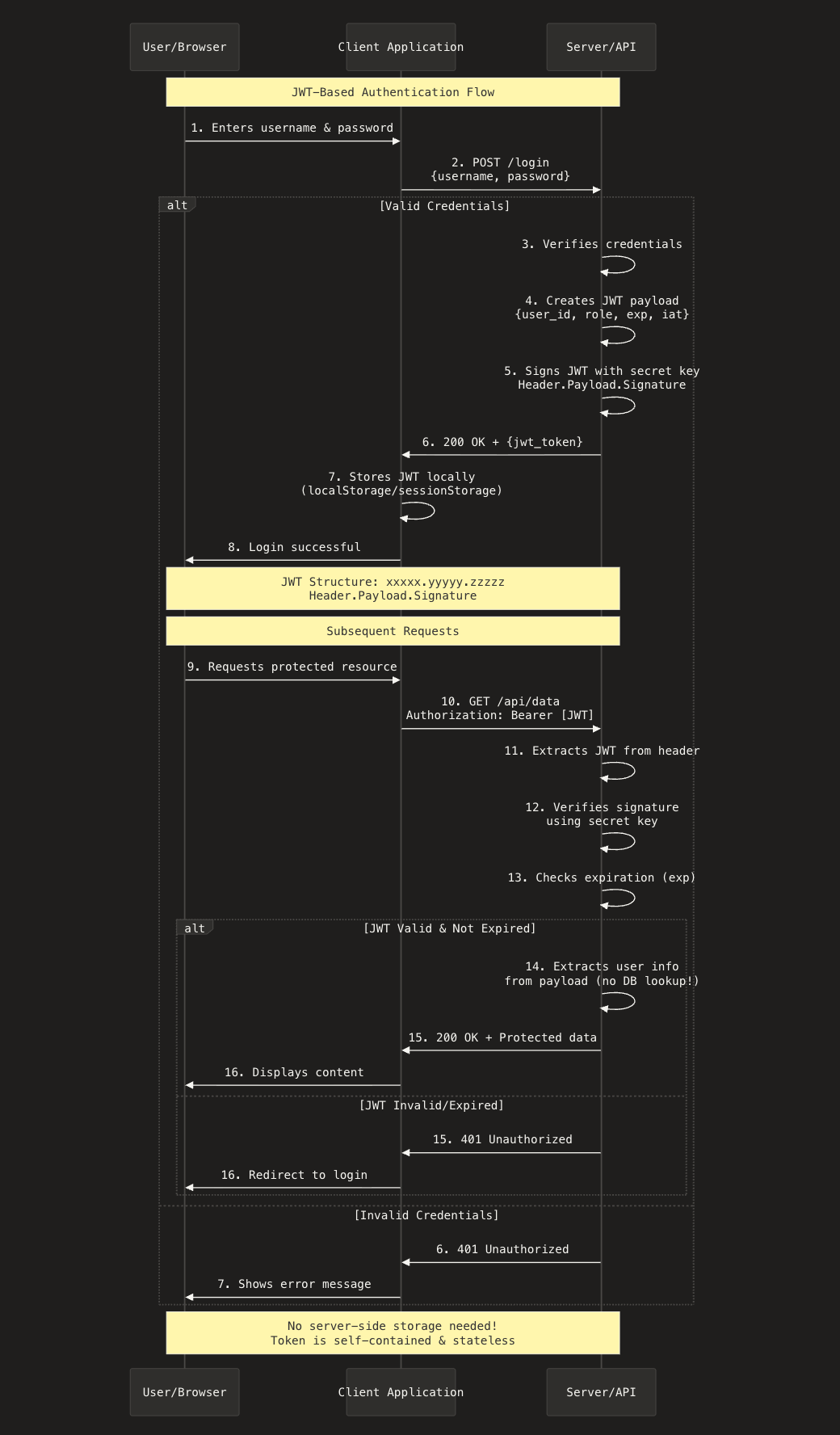
JSON Web Tokens is one of the forms of token-based authentication mechanisms and a widely used authentication technique that is used to securely share information between client and server.
How it works.
The JWT works just like any token-based auth strategies. The only difference is how the token is generated. The JWT token primarily has three components, separated by a "."
headers.payload.signature- Headers
The headers tells what type of token this is and which algorithm is used to sign it. Example:
{
"alg": "HS256",
"typ": "JWT"
}
- alg → hashing algorithm (HS256, RS256, etc.)
- typ → type of token (JWT)
After Base64URL encoding, it becomes something like:
eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9
- Payload
The payload contains the actual data (claims) you want to store inside the token. Example payload:
{
"sub": "123456789",
"name": "Sajan Karki",
"role": "admin",
"exp": 1735689600,
}
After Base64URL encoding it becomes something like this:
eyJzdWIiOiIxMjM0NTY3ODkiLCJuYW1lIjoiU2FqYW4gS2Fya2kiLCJyb2xlIjoiYWRtaW4iLCJleHAiOjE3MzU2ODk2MDB9
- Signature.
The signature ensures that the token was not modified and was created by the legitimate server. It is created by hashing:
Base64(header) + "." + Base64(payload)
with a secret key (in HS256) or private key (in RS256).
For example:
HMACSHA256( base64UrlEncode(header) + "." + base64UrlEncode(payload),
secret)
Which becomes a long Base64URL string like:
TJVA95OrM7E2cBab30RMHrHDcEfxjoYZgeFONFh7HgQ
Final JWT format.
Putting everything together: header.payload.signature. Example JWT looks like this below:
eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJzdWIiOiIxMjM0NTY3ODkiLCJuYW1lIjoiU2FqYW4gS2Fya2kiLCJyb2xlIjoiYWRtaW4iLCJleHAiOjE3MzU2ODk2MDB9.TJVA95OrM7E2cBab30RMHrHDcEfxjoYZgeFONFh7HgQ
Sequence diagram of how JWT authentication works.
4 - Open Authorization (0Auth).
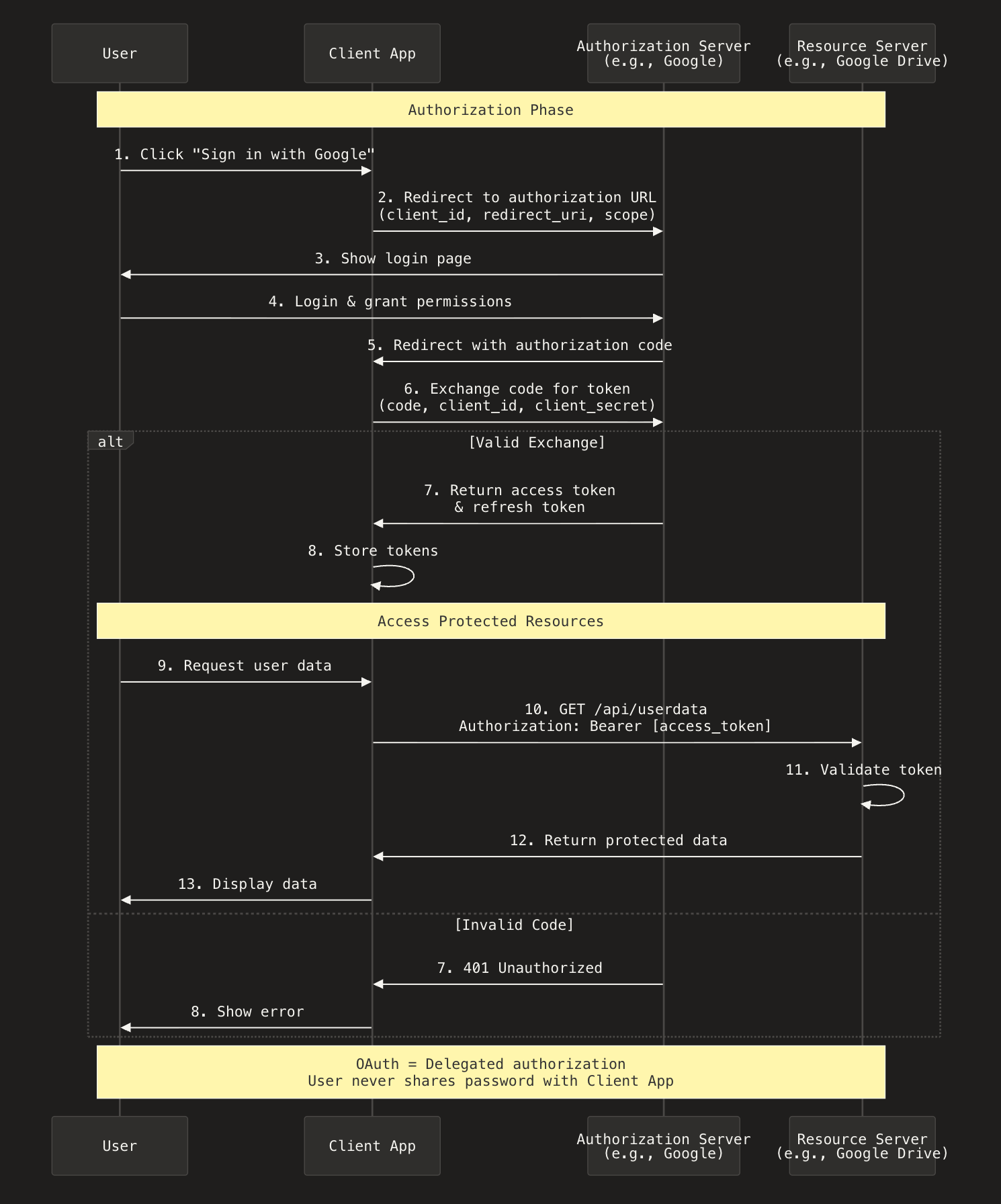
OAuth (Open Authorization) is an open standard that allows one application to access resources or data on behalf of a user, without needing the user’s password.
In other words,
OAuth allows you to log into an app using another service (like Google, GitHub, or Facebook) without giving that app your actual login credentials.
OAuth involves four main components:
- Resource Owner - That's you, the user.
- Client - The third-party app requesting access (The app you want to use).
- Resource Server - Where your data lives (Facebook's or Google's servers).
- Authorization Server - The service that verifies your identity and grants access tokens (also Facebook or Google in this case).
How it works.
- You click "Sign in with Google" - You're using an app (let's say Canva)that needs access to something from your Google account. Instead of creating a new password, you click the "Sign in with Google" button.
- Google asks for your permission - You're now taken to Google's website where you log in safely. Google then shows you exactly what Canva is asking for, like "access your email address" or "view your Google Drive files."
- You say yes (or no) - If you click "Allow," Google creates a special authorization code and sends it to Canva. This code proves you gave permission.
- Canva gets a secure access token - Behind the scenes, Canva uses that code to get an "access token" from Google. Think of this token as a temporary key card that only opens specific doors you approved.
- The app can now access what you approved - Canva uses this access token to fetch only the information you agreed to share - nothing more, nothing less. Your Google password stays private the entire time.
Sequence diagram of how Open authorization works.
Conclusion.
Choosing an authentication strategy is one of the crucial steps for application security. Basic authentication is straightforward but lacks security, while token-based authentication like JWT offers a high level of security and scalability for modern applications but requires careful implementation of token management and security practices.

Comments ()